Cybersecurity Implementation Plan
Number of words: 3348
Introduction
Island Banking Services merged with Padgett-Beal to form PBI Financial Services (PBI-FS). Padgett-Beale needs a Cybersecurity Implementation Plan for PBI-FS, which this document prepares. The department of merger and acquisitions at the company has assessed the existing cybersecurity infrastructure at Island Banking Services and discovered it lacks any formal IT security program. Furthermore, the company also conducted an inventory of digital assets and reviewed all service contracts involving the assets. These assessments showed the company’s need for an effective cybersecurity implementation plan to help detect and address the currently existing security vulnerabilities and risks.
PBI-FS plans to open a new firm on an island. Before any operations begin, the company should first develop a proper cybersecurity management plan. The plan must address such issues as security controls, software updates, hardware, as well as finding risk-reducing solutions. It should also consider the U.S. banking standards to adhere to compliance mandates. This paper provides the steps that the company should follow to address security vulnerabilities, risks, as well as its compliance with the legal framework and operability. Particularly, the plan should deal with the internal and external threats and develop a clear procedure for implementing the security apparatus in the company’s system. Cybercriminals often target the financial services sector because of the potential huge reward, and therefore, PBI-FS has to prepare for such cyber-attacks by equipping itself with a robust security structure that can effectively detect, address, and prevent future risks.
Goals & Objectives
This cybersecurity management plan (CMP) has several goals and objectives, which will be categorized into two. The first goals and objectives are concerned with the everyday business operation of PBI-FS, as discussed below:
Monitoring
The PBI-FS network will be under constant monitoring for any threats with the help of warning detection systems and an antivirus software. This helps to protect all confidential data in the company’s database and keep them secure. Implementing such monitoring solutions is crucial for mitigating the vulnerabilities and risks to company data (Lago, 2019).
Transparency
It is important for all staff members, executives, and shareholders to communicate and collaborate with each other. Effective communication helps to build trust among all parties, and as a result, making it easier to form a clear strategic picture that reassures the investors and shareholders (Lago, 2019).
Assessment
One of the initial steps that the company should do is assessing the available security strategies and resources to identify the areas that need enhancements. The security environment of PBI-FS should be carefully reviewed to ensure its daily operations are efficient and secure (Lago, 2019).
Collaboration
All departments and employees at PBI-FS should work collaboratively to build a competent team to help the cybersecurity strategy succeed. The skills and knowledge of each staff member can be put together to support the objectives and goals of the business. Also, the company should train the PBI-FS workforce on how to effectively implement the plan. This can substantially increase the plan’s success (Lago, 2019).
The second goals and objectives are project oriented, focusing on the groundwork necessary to implement the plan, as described below:
Designating Security Systems
The form must choose specific security systems before implementing the CMP, and must comply with the legal requirements. They must also be flexible to the aspects of the plan. Ensuring these measures will help protect the integrity and confidentiality of all PBI-FS data.
Designating Security Procedures, Controls, and Solutions
It is important for the company to identify the most suitable security procedures, controls and solutions before implementing the CMP. These controls are crucial for mitigating risks and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Training and Education
Training programs are important to equip employees with all the skills and knowledge they need to work efficiently. Training PBI-FS staff members on effective ways of implementing the cybersecurity plan will help create a vigilant and dynamic security culture at the company.
Scope
Although the PBI-FS is located on an island outside the U.S. main land, it is still within the country’s jurisdiction. This strategy only applies to PBI-FS, and no other Padgett-Beale office is allowed to use it. Once everything at PBI-FS is set up, the firm will start providing financial services. The plan will be important in addressing the internal and external threats, and also recommend effective methods for securing the systems, networks, and hardware. Furthermore, this strategy assesses and reviews the current weaknesses in the firm’s system and recommends proper solutions for minimizing the identified threats.
Assumptions
Below are some of the project assumptions of PBI-FS:
One of the most common targets of cyberattacks today is the financial services sector. The cybercriminals know that there is a huge financial gain potential from attacking firms in this sector, and for this reason, more of them are attracted to attempt an attack. Therefore, PBI-FS should expect a significant number of cyber-attack attempts and formulate measures to avert the threats. According to SSE (2020), “banks and financial organizations were the targets of nearly 26% of all malware attacks measuring greater than 27 other industries.”
Internal threats are a predominant in most organizations, and they pose serious risks. Island Banking Services had previously experienced insider threats that caused its bankruptcy, which means that this threat is relevant that should be addressed adequately.
Since PBI-FS operates in the financial services industry, its reputation faces high risks. “A breach of company confidential data will likely result in consumers losing trust in Padgett-Beale which will have an enormous negative effect on the organization as a whole” (RSI, 2019). The firm must, therefore, mitigate all security risks that threaten its reputation.
Constraints
There are several project constraints that should be considered by the cybersecurity management plan as described below:
Time
Arguably, time is the most limiting factor in any project. The amount of time set to implement a strategy can determine its success or failure. The plan in this case involves a high level of complexity, and therefore, it will set a reasonable time frame for its full implementation.
Finances
The financial budget allocated will determine whether the proposed strategy will be successful or not. The money set aside for the project is insufficient, considering all the software, hardware, licenses, applications, and systems needed to properly implement the CMP.
Legal
“The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) 31 USC 5311, the Foreign Assets Control Regulations (OFAC) 31 CFR 500, and the Title 31 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 103 are some of the regulations and laws that controls PBI- FS” (Lipner & Lampson, 2016). PBI-FS is also compliant with the laws of other legal international data security standards like the “International Organization for Standardization/International Electro-technical Commission (ISO/IEC) 27001” and “Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS),” which constraints its operations (Lipner & Lampson, 2016).
Project Management Plan
People
Policy
Besides providing the company with a reliable workforce, PBI-FS staff poses a significant threat to network, company data, and systems security. On the one hand, if staff members are trained and educated, they can detect insider threats, security weaknesses, and other risks, helping to improve the company’s security environment. On the other hand, internal threats can come from staff members through accidental or purposeful actions for personal gain. Proper management of the company employees can be implemented through policy. Policies and procedures will educate staff as well as hold them accountable for the actions they take (Lord, 2020).
Access
It is important for a company to limit staff access to confidential data. This can be accomplished by separation of duties, so that only specific employees can access confidential data. This will prevent employees from gain access to the data that is beyond their authorization. Implementing access control and auditing solutions can also protect PBI-FS’s confidential data and intellectual property from unauthorized personnel.
Authentication
PBI-FS will implement the multi-factor authentication system to prevent the unauthorized use of IoT devices by workers. The financial services data are confidential and must therefore be protected with strong passwords and biometric verification systems. This will significantly reduce authentication susceptibilities. Also, strong authentication enables the IT department to track employee actions and access within the workplace network.
Point of Contact
Any discoveries, concerns, or questions related to cybersecurity should be directed to the IT department. The interim CISO will handle all concerns and questions about this Cybersecurity Implementation Plan. The CISO can be contacted by phone: 212-509-6995, email: CISOPBIFS@IS.com.
Processes
Transactions
Transactions pose fraudulent risks that will require the dual authorization verification to protect them against any deceit. Fraudulent transactions are highly likely and can potentially damage the reputation of PBI- FS. The dual authorization verifies the sender and receiver and ensures the transaction is legitimate. This process is especially critical for large financial transaction amounts.
Banking Sessions
Currently, all banks operating online have significant vulnerabilities. According to a recent survey, “61% of tested online banks have minimal protection, and of the online banks surveyed, 54% had vulnerabilities in online banking sessions” (PT, 2019). PBI-FS faces the risk of hackers intercepting confidential data during its online transmission from one point to another. Cybercriminals can hijack a banking session or identify an insecure protocol through which they can gain access to compromise the session. “The HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) or HTTP Public Key Pinning (HPKP) should be adopted and implemented to minimize the possibility of sensitive data interception during online banking sessions” (PT, 2019).
Technologies
Firewall
A firewall is an important structure in any organization with online operations as it protects computers, devices, and workstations from external threats. “This is done through the manual selection of ports that receive and send data” (CRT, 2019). As a result, the firewall mitigates data risk as it constantly monitors the company’s network traffic to detect and stop suspicious activities. It protects data, applications, and users.
Antivirus
An antivirus software should be implemented in the company’s network system to mitigate the potential vulnerabilities and risks. The risk of malware incursion poses a tremendously costly threat, but this can be averted with the use of a quality antivirus solution (WEBROOT, 2020).
Encryption
Encryption helps to deny malicious users access to a private network, thus maintaining data confidentiality and integrity. A symmetric key will be used to encrypt all moving data to ensure its security while in transit. If a hacker manages to intercept the data during transit, they will require a decryption key to make the data usable (Lord, 2020).
Secure Socket Layer
“This is a transport-level security solution that establishes a secure connection between a server and the web browser” (Bhakhra, 2019). This security measure manages the apparatuses that encode data to protect it during transit. The encrypted connection ensures the data being transferred remains secure from attack susceptibilities (Bhakhra, 2019).
Intrusion Detection
The intrusion detection systems is another important cybersecurity structure that provide invaluable monitoring capabilities. The IDS continually scans the network to detect anomalies, vulnerabilities, and risks and immediately alerts the IT personnel in case of an issue. The IDS will also monitor the company’s network traffic and systems in search of known threats and suspicious activities (Pratt, 2018).
Strategy Implementation
Security Controls
Security Controls comply with the pertinent regulations to protect company networks against security threats (Breen, 2019). Below are some of the security controls recommendations that PBI-IS will implement to address potential vulnerabilities in its business operations. Security controls ensure the data confidentiality and integrity.
Mandatory Controls
Access Control: “Access control ensures security through the following five main components: audit, manage, access, authorization, and authentication” (Tunggal, 2020). These controls can be physical, logical, or both. A user can have access to designated resources based on their authority and access privileges. Access control authenticates the approval of a user’s access request to ensure they have proper authorization. Not all users have the same privileges, and this enables easier maintenance of data security. Therefore, access controls are crucial for mitigating access-associated risks (Tunggal, 2020).
Data Backup: Backup services help to maintain data availability and integrity. In case the company’s network suffers a cyber-attack, or a compromise of its operations, the backup system can help to retrieve crucial data. PBI-FS should have a layered security strategy that gives it access to secured data. PBI-IS’s network should be protected with an encrypted backup solution to secure its confidential data (CT, 2020).
Compensatory Controls
Firewall: Adding a firewall solution to PBI-IS’s network provides a crucial perimeter defense for its confidential data. It isolates external threats by enabling manual control of ports. This helps to protect data, applications, and users from various threats (CRT, 2019).
Virtual Private Network: A VPN encrypts the internet connections between devices in a network. A VPN structure will be developed in PBI-IS’s network to secure connections in its network and ensure data security and confidentiality during its transmission. “Specifically, a VPN is beneficial to any company employee who needs to make a connection remotely” (CISCO, 2020).
Incident Response Plan: PBI-IS will implement an IRP to test and establish the procedures for reducing the impact of a security breach from internal or external threats. Some of the important aspects that the plan must emphasize are agility, adaption, and anticipation to address the various vulnerabilities. PBI-FS must implement the IRP to remain proactive.
System Development Life Cycle and Schedule
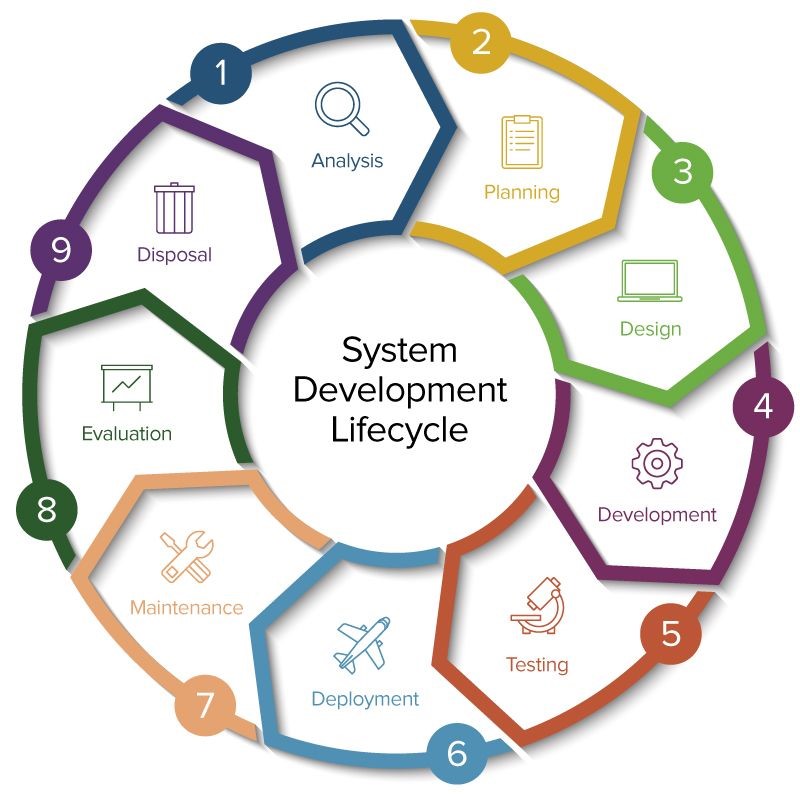
Figure 1: System Development Lifecycle (SMARTSHEET, 2020)
“The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) provides a step-by-step guide of the phases involved in implementing systems that are either software-based or physical” (SMARTSHEET, 2020). There are several models that outline the phases of SDLC, such as Figure 1 above. The structure of every SDLC model is phased, and can be adapted to fit an organization’s needs (SMARTSHEET, 2020). “The following seven-phase SDLC model is the most common and widely used: planning, systems analysis & requirements, system design, development, integration & testing, implementation, and operations & maintenance” (IA, 2020).
Milestones
A milestone is combined with control gates to help show evaluated progress. “A control gate is a point in time during the system development process that evaluation is conducted so that management can determine a course of action” (ISC, 2009). The management can allow the current development to continue, change its course, or stop it altogether. Conducting a control gate between major phases or stages represent the SDLC milestone. These milestones illustrate the measurable success of the executives and stakeholder, as well as the progress of the evolving system.
Resource Requirements
Projecting the exact cost of all suggested solutions and procedures for implementing this cybersecurity plan is difficult. However, the firm can consider certain important factors. First, this strategy purposes to mitigate PBI-FS security risks. Secondly, the cybersecurity plan is intended to alleviate serious vulnerabilities that threaten the company’s data, customers, reputation, and finances. The plan has also conducted a cost to benefit analysis of the proposed solutions and decided they are all necessary.
Enterprise IT Architecture
Hardware
The current workstations are older than five years and run on Windows 8.1., meaning that they have not been updated for a while, thus making them less efficient. PBI-IS should either purchase new workstations or upgrade the old hardware. The plan recommends a case-by-case approach to address these problems. It also recommends the hiring of an external company representative to assess the workstations’ current state to determine a cost-effective decision for PBI-FS. A firewall protection is also needed to provide crucial perimeter defense for the company’s network infrastructure.
Software
All workstations currently use Microsoft Office 2019. Most of the anti-virus business licenses obtained from the merger are under investigation, and it has already been discovered that about 10 workstations were operating with unauthorized anti-virus software. Therefore, PBI-IS needs to purchase new anti-virus software licenses for efficient network protection.
Network Infrastructure

Figure 2: Network Infrastructure
Cybersecurity Defense
The following are some of the recommendations for procedures and processes to ensure PBI-IS has a layered network security defense:
Training & Awareness
It is important for the company to provide training programs to the staff to create a security culture at the workplace. This will help to mitigate most of the existing workplace risks and reduce insider threats. The employees should understand the cybersecurity threats that the company potentially faces and their consequences. They should also know what to do to prevent these risks.
Encryption
Encryption is a basic measure in system security, but it is very effective in ensuring data protection during its transmission over the network. It will help to maintain PBI-IS data security, integrity, and confidentiality.
Intrusion Detection System
The IDS will help to monitor the company’s network for potential risks and susceptibilities. It continually scans the network to detect anomalies, vulnerabilities, and risks and in case of an issue, immediately alerts the IT department. The IDS will also monitor the company’s network traffic and systems in search of known threats and suspicious activities (Pratt, 2018).
References
Bhakhra, S. (2019). Secure Socket Layer (SSL). Geeks for Geeks. Retrieved from, https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/secure-socket-layer-ssl/
Breen, C. (2019). Developing an Effective Cyber Security Management Plan. WBM Technologies. Retrieved from, https://www.wbm.ca/blog/article/developing-an-effective-cyber- security-management-plan/
Britt, P. (2017). Cybersecurity Risk Management: Finding and Fixing Your Security Vulnerabilities. eSecurity Planet. Retrieved from, https://www.esecurityplanet.com/network- security/cybersecurity-risk-management.html
CF, (n.d.). (2020). Example Cybersecurity Risk Management Plan. Compliance Forge. Retrieved from, http://examples.complianceforge.com/example-risk-management-program-rmp.pdf
CISCO, (n.d.). (2020). What Is a VPN? – Virtual Private Network. CISCO. Retrieved from, https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/vpn-endpoint-security-clients/what-is-vpn.html
CRT, (n.d.). (2019). Barracuda Firewall: An In-Depth Review. CR-T. Retrieved from, https://cr- t.com/blog/barracuda-firewall-an-in-depth-review/
CT, (n.d.). (2020). Backup and Disaster Recovery. Corsica Technologies. Retrieved from, https://www.corsicatech.com/solutions/it-services/backup-disaster-recovery/
IA, (n.d.). (2020). The Seven Phases of the System-Development Life Cycle. Innovative Architects. Retrieved from, https://www.innovativearchitects.com/KnowledgeCenter/basic-IT- systems/system-development-life-cycle.aspx
Lago, C. (2019). How to implement a successful cybersecurity plan. CIO. Retrieved from, https://www.cio.com/article/3295578/how-to-implement-a-successful-security-plan.html
Lipner, S., and Lampson, B. (2016). Risk Management and the Cybersecurity of the U.S. Government. National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved from, https://www.nist.gov/system/files/documents/2016/09/16/s.lipner-b.lampson_rfi_response.pdf
Lord, N. (2020). What Is Data Encryption? Definition, Best Practices & More. Digital Guardian. Retrieved from, https://digitalguardian.com/blog/what-data-encryption
Pratt, M. (2018). What is an intrusion detection system? How an IDS spots threats. CSO. Retrieved from, https://www.csoonline.com/article/3255632/what-is-an-intrusion-detection- system-how-an-ids-spots-threats.html
RSI, (n.d.). (2019). The Many Cyber Security Threats to the Financial Sector. RSI Security. Retrieved from, https://blog.rsisecurity.com/the-many-cyber-security-threats-to-the-financial- sector/
SMARTSHEET, (n.d.). (2020). The Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Using a System Development Life Cycle. Smart Sheet. Retrieved from, https://www.smartsheet.com/system- development-life-cycle-guide
SSE, (n.d.). (2020). The Biggest Cybersecurity Risks In The Financial Services Industry. SSE. Retrieved from, https://www.sseinc.com/cyber-security/the-biggest-cybersecurity-risks-in-the- financial-services-industry/
Tunggal, A. (2020). What is Access Control? UpGuard. Retrieved from, https://www.upguard.com/blog/access-control
WEBROOT, (n.d.). (2020). What is Antivirus Software? Webroot. Retrieved from, https://www.webroot.com/us/en/resources/tips-articles/what-is-anti-virus-software