Essay on Challenges of UK Government Related to COVID Campaign
Number of words: 3878
The Coronavirus pandemic has had adverse effects on certain nations of the world, especially due to the weak healthcare system followed by them. In accordance with the rising mortality rate and chaos, the decentralisation and division of certain countries’ healthcare systems is taking place. Vulnerable and weaker sections of society have been adversely affected due to the onset of the pandemic which is expected to continue for a substantial amount of time. Even though the UK government adopted a steady plan to counter the ill effects of the covid crisis, certain challenges were faced by them irrespectively.
Hindered implementation of SOPs
Due to the pandemic, the ability of people to meet and communicate face to face has been curbed. The rise in protests due to certain regulatory changes implemented by the government has also created a problem. The enraging population has been faced with a strict police force and heavy fines for their actions. The SOPs given out by the government faced huge lashes from the public, thus becoming a challenge for the UK Government in facing the coronavirus pandemic. The necessary protection from the virus was countered with another issue, namely, the psychological impact of being isolated and away from society (Baines et al., 2017). It is of the opinion of certain public health directors that the only way of generating and uplifting the population’s confidence was to adopt an honest and clear approach in the deliverance of messages and decision making processes. This strategy for clear and straightforward communication between the public and the government has also been adopted by subsequent local leaders, paving the way for an effective manner of handling such healthcare issues in the future. Thus, it can be said that the following of proper SOPs is of high importance in the smooth handling of such a pandemic situation to minimise severity (Fucks and Diamantopoulos, 2010). The hindrances caused by the public has affected the UK government severely due to the malfunctions in implementations of policies, strategies, plans, and other activities.
People’s Mistrust in the vaccines
Even though the vaccine has been developed quite quickly, the job of providing these vaccinations to people is accompanied with major issues in the distributions, deployment, and public acceptance. It is considered the job of the Government to educate people in matters Like the merits of taking vaccinations, safety procedures, and after effects. The government must counter the rising mistrust among people in regards to taking the vaccine. This should be achieved through good and smooth communication. The government needs to generate closer communities and a trustworthy environment through the successful administration of vaccinations amongst the population of the UK. Certain guidelines pave the way for efficient vaccination confidence and the programs of the government to administer them. They are
- Public belief regarding the safety of vaccines
- Trustworthiness of the institutions conjuring the vaccines
- Vaccine Distributions, deployment, and administration processes followed by the government
- Maintaining efficient communication and public trust by regulatory bodies.
Effectiveness of British government’s Vaccination and COVID strategy
To create safe and efficient vaccinations, the UK is at the vanguard of a massive multinational endeavor. Chief scientific advisor Sir Patrick Vallance conceived up the Vaccine Taskforce, which was designed to accelerate vaccine research and development in the UK and abroad. As of May of 2020, the Vaccination Taskforce was formed under the Department for Commerce, Energy & Industrial Strategy, and was asked to execute, reporting directly to the Prime Minister, and collaborating with Deputy Chair Clive Dix. For each vaccine type, the Vaccine Taskforce can obtain enough doses to vaccinate the required UK population. Those older than 50, healthcare and community professionals who are on the front lines, and individuals with underlying illnesses should be vaccinated, according to preliminary guidance from the UK’s Joint Committee of Vaccination and Immunisations. According to Joint Committee on Vaccination & Immunization guidelines and drug testing, the exact dose necessary will be ascertained. Most vaccines are expected to require two doses, and the government is exploring whether yearly or periodic revaccination booster injections would be required to ensure persistent protection against disease. COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers vary from tiny laboratory startups to large pharmaceutical companies, each with varied commercial aims and financing levels to facilitate production scale-up and medical testing To assist these operations, the Vaccine Taskforce invests money on the line in certain circumstances, while in others, it successfully established an early purchase arrangement. Most government financing is tied to medical, administrative, and other benchmarks in both instances of funding. The funding will be cut off if a vaccination does not prove to be effective. Over 295 000 individuals have enlisted in the National Health Service COVID-19 vaccination registry to assist speed up the development of effective vaccines. In addition to financing medical testing of crucial significance, such as Janssen’s two-dose Ad26 protocol (NCT04505722), Imperial College London’s self-amplifying RNA (ISRCTN17072692), and Valneva’s whole aerosolized vaccine, the government plans to stimulate enrollment in disease locations with smartphone research teams notified by robust PCR testing, and has raised funds for drug testing of great significance.
The government has facilitated the establishment of formalised, credentialed assays, such as quantitative high-throughput spike-protein ELISAs, live viral-neutralisation laboratory tests, and T-cell assays, which will be readily accessible to all immunisation developers in order to reconcile outcomes from the numerous drug testing and to better comprehend immunologic corresponds of safety. The world’s vaccine manufacturing capacity is fundamentally flawed for the hundreds of millions of doses that are required, and the UK’s manufacturing capability has been equivalently limited. This presents a major challenge. For the UK population to receive a new vaccination within nine months of the pathogen’s discovery, the Vaccine Taskforce has secured funds for adaptable and surge production in many new UK vaccine manufacturing locations. To prepare for the upcoming pandemics, the government also wants to introduce new vaccination technology and abilities to the UK. Every person on the planet who is at threat of SARS-CoV-2 illness will have access to reliable and efficacious vaccines because of the UK. The COVID-19 Vaccinations Global Access Facility, to which the UK has pledged £548 million, will provide vaccination for the Population of the uk and offer access to vaccines for lower-income nations: eventually 2 billion dosages for 1 billion people across the world. Gavi, Vaccine Alliance, Alliance for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, WHO, and a comprehensive partnership of 175 countries work together to enhance the possibilities of getting access to a vaccination and making it accessible for everyone who is in need of one. Four coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccines have now been approved for use in the UK.
It has now been determined that four coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccinations can be used in the United Kingdom. As components of the approval process, extensive tests have been conducted to evaluate the antibody reaction, health impact, and effectiveness of these vaccines. In place to ensure that clinical and public health advice on the immunisation programme is based on accurate data, vaccines must be continuously monitored as they are brought out in the community. For the COVID-19 immunisation project, Public Health England (PHE) collaborates closely with the Medicines and Healthcare Regulatory Agency (MHRA), NHS England as well as other government, devolved administration, and partner organisations. According to several trials in the UK, a single dosage of either vaccine is somewhere between 55 and 70 percent efficacious against symptomatic sickness, with greater levels of protection against deadly infections such as hospital readmission. After a second dose, more resistance is found. Several studies have shown that vaccines are efficient in preventing illness and spreading.
Each of the COVID-19 vaccines authorised in the UK has undergone extensive medical testing, which have shown that they are extremely effective in avoiding symptomatic disease in the groups investigated. To ensure vaccines are successful in the real world, it is essential to maintain evaluating their performance in clinical trials and in the field. So that successful vaccinations can be administered as quickly as feasible, clinical studies are also conducted in order to determine the effectiveness of the vaccine against laboratory verified symptomatic disease with a reasonably short follow up duration. When it comes to choosing which vaccines to use, who to offer them to, and whether booster doses should be given, evaluating their efficacy against various results (such as severe disease and onward transmission) and comprehending the length of immunity is crucially significant. By contrasting disease rates in vaccinated and unvaccinated persons, the efficiency of vaccines is assessed. Listed below are the most recent real-world research on vaccine effectiveness conducted in the UK. It is important to note that most of these data are from when the Alpha form was prevalent; nevertheless, growing data on effectiveness against symptoms is presented in the picture below.
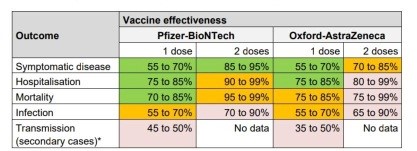

Figure 1: Vaccine Effectiveness
Source: (Public Health England, 2021)
Comparison of Uk with other country’s digital strategies:
| United Kingdom’s strategies to stop the spread ● Covid-19 spread portfolios were created using the digital strategy by Uk. SOPs were also taught to the public by the UK government, which held a number of seminars. In contrast to Pakistan’s policy, this was the UK’s best tactic. | Pakistan’s Strategies to stop the spread ● The tiger force was Pakistan’s tactic to increase awareness. They went from house to house, telling people how important it was to stay home and obey the SOP’s. As a result, there was a risk of spreading the coronavirus. |
| ● It was decided that the next step would be to spout facts to educate the populace about the vaccine’s reliability. Many physicians conducted online meetings to educate the public about the vaccination. | ● When it came to this element of the plan, Pakistan came out on top. That’s because the celebrities, tiktokers, and entertainers were paid to participate. The government provided a small amount of money to these individuals and requested them to get vaccinated as a condition of receiving it. As a result, all of their followers will get vaccinated. As a result, the immunisation technique was more effective. Vaccine trust grew as individuals posted photos of themselves getting vaccinated on social media networks. |
| ● To prevent people from doing their business online instead of coming to their jobs, the last solution was to create a digital strategy. Proper agreements were made to achieve this. Many new applications have been released in the past few months. On-line attendance systems were developed as well as new attendance monitoring tools. | ● There was a crackdown by the Pakistani authorities on people leaving their homes. There was a lockdown, and the poor and needy were frantically trying to find food to survive. This idea wasn’t as good as the one proposed by the United Kingdom. |
Table 1 ( Comparison of Uk with other country’s digital strategies)
Source: (By the Author)
Digital communication strategy related recommendation
Since awareness and understanding alone rarely affect behaviour, the profession of media marketing is based on extensive study. Effective behaviour change requires the adoption of tactics that aim to overcome obstacles and offer people with personal, meaningful motivators. Marketing tactics can be more efficient by recognising behaviours that must be changed to accomplish a program’s objectives, fragmenting audiences based on who is most likely to change their behaviour (or not yet participating), and attempting to address the obstacles to behaviour change while also helping to ensure that an audience is sufficiently engaged.
Community-based digital marketing can be utilised to reduce hurdles and urge people to acquire their third dosage of COVID-19 vaccination, DRIP model has been used to provide quality recommendations as described below:
Differentiate the assistance
In order to determine or identify other similar services, it is focused on prioritising a certain service. It will be mandatory for the government of the United Kingdom to employ vaccination as a technique to allow people to walk outdoors securely. When compared to other marketing settings, the situation is complicated. Working from home and following COVID safety practise will have to be differentiated from getting vaccinated. Individuals will be more motivated to get vaccinated as a result of this. Contemplate distinguishing vaccinations as a means of achieving speedy recovery from the unpleasant Covid circumstance will be advantageous in terms of creating favourable perceptions from those who receive them.
Reinforcement of statements
As a result, customers will be able to ask questions and get answers about the entire process by using the application. Here, government officials can create a 24-hour customer service centre to answer questions from the public. Incorporating celebrity endorsements into this approach can improve it. The government can use a celebrity’s image to encourage vaccinations to the general public by using his or her image. In this sense, the government will be expected to utilise suitable and effective safety procedures.
Changes in CSR policy of Pfizer
In light of the pandemic, the competition amongst pharmaceutical giants in order to create an effective and safe vaccine against the coronavirus had risen to great lengths. This needed certain thorough changes in the CSR policies, communication strategies and related practices of the pharmaceutical companies like Pfiezer, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, and so on. Through the effective mRNA technology possessed by companies like Moderna and Pfiezer, the ability to conjure up an effective vaccine is highly possible on their part. In regards to the growing losses, unemployment issues and lifestyle degradations caused by the pandemic in the lives of the people, the rise in stock market value and the public image of the pharmaceutical companies was boosted with the need for a vaccine.
Pfiezer is known for certain effective medications developed by it like Advil, Celebrex, Lyrica, Viagra, and Robitussin. The company has emerged from an all in one shop to a global giant in the pharmaceutical industry in regards to its effective productions and medications which has gained the company immense success.
In regards to the covid 19 vaccine, the company is working with an aim of providing fair and affordable accessibility of the vaccines to the people of the world. Ever since the inception of the vaccine programmes, Pfizer has been contacted by over 100 nations and organisations regarding the vaccines. Nations like Peru, Chile, Cambodia, and Mexico with emerging markets for vaccines have entered into supply agreements and other negotiations with Pfiezer.
Pfizer collaborated and acted upon a COVID-19 vaccine developed in April 2020 along with BioNTech. The mRNA vaccine developed is called BNT162b2. Phase 3 clinical studies have demonstrated a safe administration and the subsequent efficacy of 95 percent of the vaccination. In order to be efficient, two dosages spaced 21 days must be administered. The results signify a significant step up in the 8-month vaccine-making process to help stop this atrocious epidemic. Dr. Albert Bourla, President and CEO of Pfizer, said in a news release that at Pfizer, they keep working at scientific rates to combine all data received so far and establish communication with authorities throughout the world. It stands under the rights of every person to receive an effective and safe vaccination against the epidemic.
The development of high demand and need for the vaccine was the turning point in the CSR policy of Pfizer. Social responsibility has risen in the company, because virtually every country now gets the vaccines created by them. Through collaborations, CSR programmes and unique initiatives, Pfizer is seeking to improve access to the most vulnerable sections of society across the world. A fair price approach should be adopted, but non-commercial means such as donations should also be employed (Porter, 2008). They have generated new systems for payment and finance, and innovative schemes to engage with governments and other key organisations to improve the patient’s results.
In the fields of transformation, reduced transaction costs and differential pricing, the firm is seeking breakthrough ideas in order to boost their vaccination programmes. In 2020, more than 700,000 persons outside the United States would have been helped by patient assistance programmes developed by Pfizer. With regulatory permission, a tiered price structure is to be created for both current and upcoming vaccinations. In line with this strategy, we are pledged by the Vaccine Alliance by 2027 to give up to 930 million pneumococcal conjugate vaccines to newborns and young children worldwide.
The communication strategies followed by the company had to be stepped up and altered in lieu of the increased communication with major nations of the world. Their communicative policies have been positively improved. When offices of a corporation are distributed around the world, employees or supervisors who work in different countries may feel separated or apart from each other or the central company. As a result, management and employees in other nations may be uncertain to raise inquiries. Sometimes certain tasks are pushed to one side. Using regular video conferencing or an effective intranet team website as part of project communication to avoid these problems is highly recommended. The creation of a virtual place of association where staff can talk and meet each other during breaks is aimed at. For this job, the company assigned competent interpreters.
The situation in India with the emergence of a high number of cases was amongst the main concerns of Pfizer. Patients demand excellent treatment throughout the country from frontline health professionals. Pfizer provided frontline and health care workers in India with over 3 lake N95 protective masks via non-profit organisations. In Maharashtra there has been a fast surge in COVID-19 cases. As a result, their testing and isolation efforts were successfully boosted by the MCGM Disaster Management Cell and Health Department. Five highly efficient Maquet Servo-I Ventilators were donated in third party hospitals with the COVID-19 facility by Pfizer and Americares India Foundation. Those are Pfizer’s efforts to help India to cope with a pandemic. Certain other developing nations have also been helped by the facilities provided by Pfizer leading to a change in the company’s structure.
Pfizer has a duty of watching their medicines closely. In accordance with company policies, All drugs are approved by professionals. Pfizer regularly and carefully supervises the supply of its medications. With over 40 Pfizer-owned locations and over 200 vendors worldwide, researchers run one of the business’ most extensive supply chain networks and offer quality as well as redundancy if necessary. The manufacturing and supply chain professionals have worked continuously to guarantee that Pfizer drugs are accessible worldwide to patients. To date, our supply chain has not been affected and all our plants in the areas concerned operate effectively without hindrances.
Pfizer has developed a full and unprecedented preparatory strategy to maintain control of the activities of the site. Whenever new information is available, they shall continue to offer timely updates. Their production has grown significantly, and a request was transferred to the essential products, and overtime was permitted in different locations due to patient demand. In addition, they have enhanced its demand surveillance and order management systems and logistics controller programmes, so that their medications and related items reach their clients in good time and in acceptable shape.
As per regional law, These agreements provide for the protection of compensation and liability, including the COVAX facility. To guarantee that all parties concerned, including government agencies, are adequately safeguarded, Pfizer negotiates compensation arrangements with governments. Insurance provisions are standard in contracts with the governments to provide vaccines during emergencies of public health, such as during the H1N1 outbreak. It is majorly intended to help governments discover solutions to ensure that a good risk balance is maintained by both sides. A lengthy history of humanitarian emergency support exists in Pfizer. In accordance with the ill effects that the pandemic has had on the population of the world, Pfizer aims to help the frontline workers and patients as effectively as possible by providing vaccines and medicines through the governments and NGOs. The company has also initiated to donate a huge sum of forty million dollars to the cause.
Reference list
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Provisional death counts for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): daily updates of totals by week and state. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/COVID19/index.htm
Baines, P., Fill, C., Rosengren, S. and Antonetti, P. (2017) Fundamentals of marketing, UK: Oxford University Press. Chapter 1, 2 and 3.
Fucks, C. and Diamantopoulos, A (2010) Evaluating the effectiveness of brand positioning strategies from a consumer perspective, European Journal of Marketing, 44 (11/12). 1763 -86
Porter, M (2008) The Five Competitive Forces that Shape Strategy, Harvard Business Review, pp 78-93
Ozuem, W and Gordon, Bowen (2016) Competitive Social Media Marketing Strategies, Hersey: IGI,Chapter 1, 2 and 5.
Stephen, A.T and T.O (2010) Deriving Value from Social Commerce Networks, Journal of Marketing Research, Vol. 47, No 2. Pp.215 – 228.
Laudon, K and Traver, C (2015) E-commerce 2015: Business. Technology. Society, Harlow: Pearson,Chapter 1, 2 & 3.
Public Health England. ‘COVID-19: vaccine surveillance strategy 2021’
Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. ‘Coronavirus vaccine – weekly summary of Yellow Card reporting 2021’
Lopez Bernal J, Andrews N, Gower C, Robertson C, Stowe J, Tessier E and others.
‘Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines on COVID-19-
related symptoms, hospital admissions, and mortality in older adults in England: test
negative case-control study.’ British Medical Journal 2021: volume 373, n1,088
Public Health England. ‘Public Health England vaccine effectiveness report – March 2021.Public Health England 2021
Pritchard E, Matthews PC, Stoesser N, Eyre DW, Gethings O, Vihta K-D and others. ‘Impact of vaccination on SARS-CoV-2 cases in the community: a population-based study using the UK’s COVID-19 Infection Survey.’ medRxiv 2021: 2021.04.22.21255913
Public Health England. ‘Public Health England COVID-19 vaccine surveillance report: 20 May 2021 (week 20)’ Public Health England 2021
Gopez, J.M.W., 2021. Building public trust in COVID-19 vaccines through the Catholic Church in the Philippines. Journal of Public Health, 43(2), pp.e330-e331.
Forman, R., Shah, S., Jeurissen, P., Jit, M. and Mossialos, E., 2021. COVID-19 vaccine challenges: What have we learned so far and what remains to be done?. Health Policy.
Baines, P., Draper, H., Chiumento, A., Fovargue, S. and Frith, L., 2020. COVID-19 and beyond: the ethical challenges of resetting health services during and after public health emergencies.
Smith, L.E., Duffy, B., Moxham-Hall, V., Strang, L., Wessely, S. and Rubin, G.J., 2021. Anger and confrontation during the COVID-19 pandemic: a national cross-sectional survey in the UK. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 114(2), pp.77-90.
Jones, A., Sergejeff, K., Sherriff, A., Teevan, C. and Veron, P., 2020. The Challenge of scaling up the European Union’s global response to COVID-19’. ECDPM brief. April.
Bryce, C., Ring, P., Ashby, S. and Wardman, J.K., 2020. Resilience in the face of uncertainty: early lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Risk Research, 23(7-8), pp.880-887.
Lawrence, K., 2021. Analyzing Pfizer’s COVID-19 Vaccine PR Strategy. SAGE Publications: SAGE Business Cases Originals.